Thermal Drift in On-Chip: Photonic crystal sensors (PCS) have gained significant traction in lab-on-a-chip technologies due to their high sensitivity and compact nature. However, one of the fundamental challenges in their deployment is thermal drift, a phenomenon where temperature fluctuations cause changes in the optical properties of the sensor, leading to measurement inaccuracies. This article […]
Category: simulation

Finite Element Analysis (FEA) plays a crucial role in optimizing the integration of photonic crystal (PhC) sensors with silicon photonics. This integration is fundamental for advancing optical sensing technologies used in biomedical applications, environmental monitoring, and high-speed optical communication. Photonic crystals, with their periodic dielectric structures, exhibit unique light-manipulation properties, such as photonic bandgaps, that […]
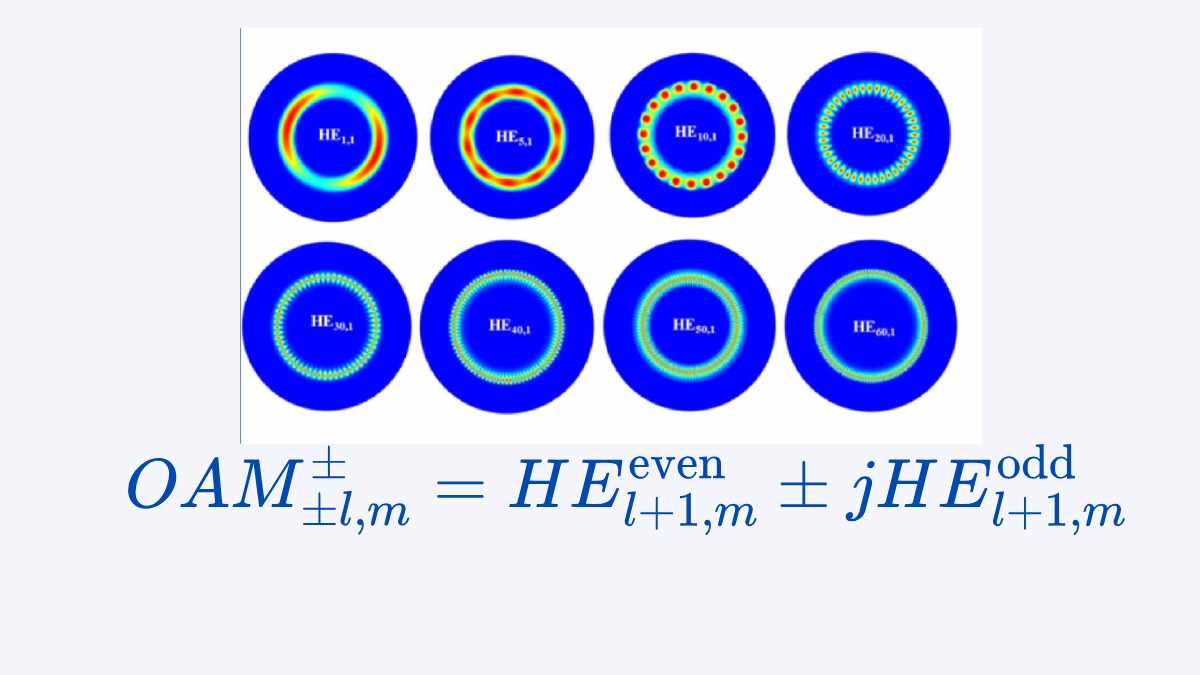
OAM Modes in Fiber : Optical fibers support different types of modes depending on their refractive index profile. In step-index fibers, the fundamental modes are linearly polarized (LP), but in ring-core fibers (RCFs), the natural modes are hybrid modes, specifically HE (hybrid electric) and EH (hybrid magnetic) modes. These modes arise due to the vector […]
Photonic crystal sensors have emerged as a promising solution for highly sensitive, miniaturized, and CMOS-compatible on-chip sensing applications. The integration of these sensors with silicon photonics platforms has enabled high-performance label-free detection of biological and chemical analytes. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) plays a crucial role in designing and optimizing photonic crystal structures to ensure their […]

Photonic crystal nanocavities (PCNCs) have revolutionized the field of integrated photonics by enabling ultra-high quality factor ($Q$) resonators for various applications, including optical sensing, nonlinear optics, and quantum information processing. The design and optimization of high-$Q$ photonic crystal nanocavities require advanced computational modeling techniques, among which Finite Element Analysis (FEA) stands out due to its […]
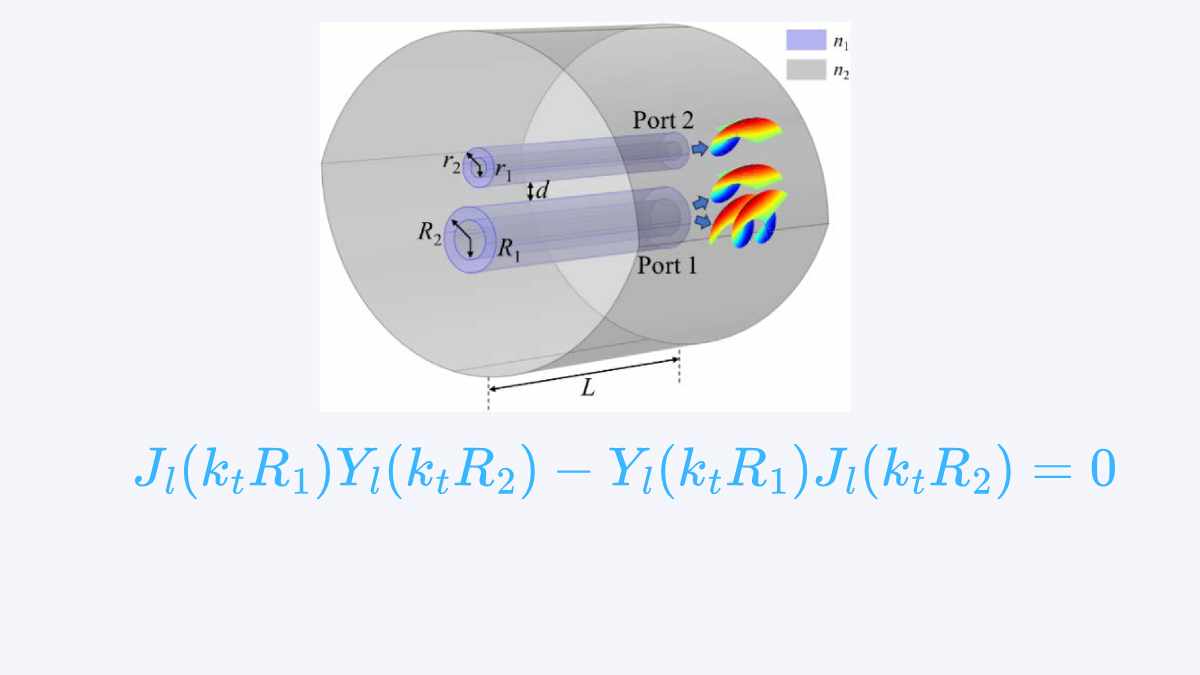
Ring-core fibers (RCFs) are a specialized type of optical fiber designed to support orbital angular momentum (OAM) modes, which have gained significant attention in optical communication, quantum information processing, and high-capacity data transmission. Unlike conventional step-index fibers, RCFs possess a refractive index profile with a core that is shaped like a ring rather than a […]
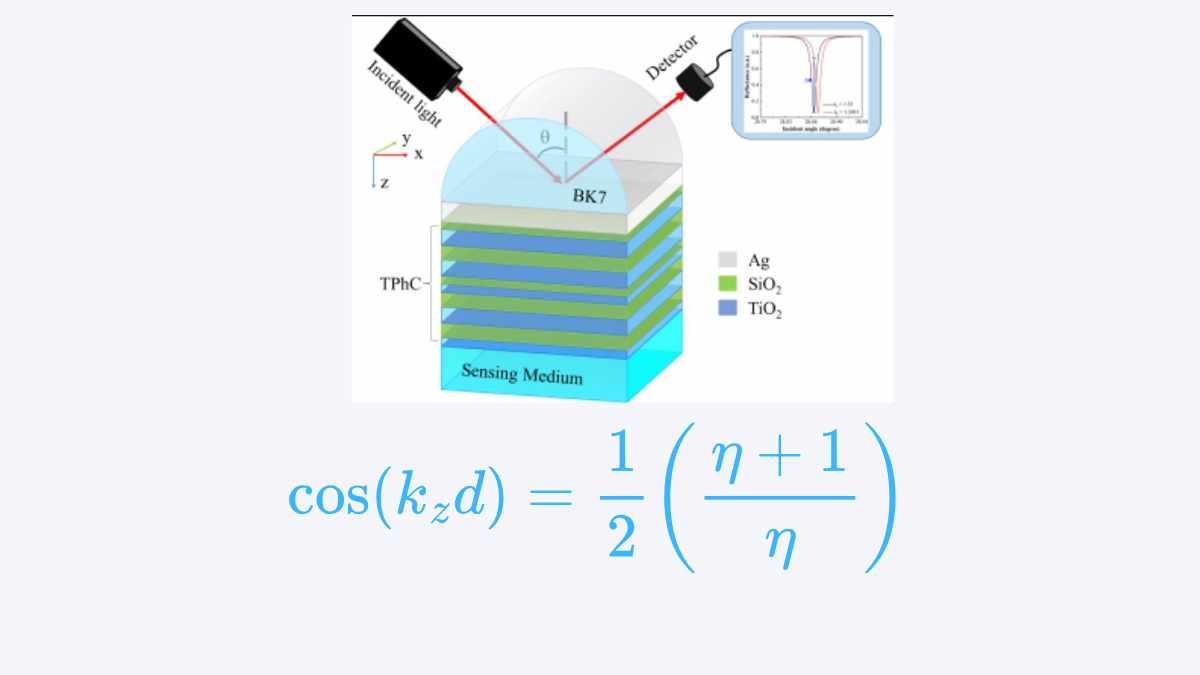
IntroductionTamm-plasmon-polaritons (TPPs) are optical surface states that arise at the interface between a metallic film and a photonic crystal (PC). Unlike traditional surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), which require specific conditions for excitation (such as total internal reflection in a prism-coupled system), TPPs can be directly excited in normal incidence configurations, making them ideal for biosensing […]
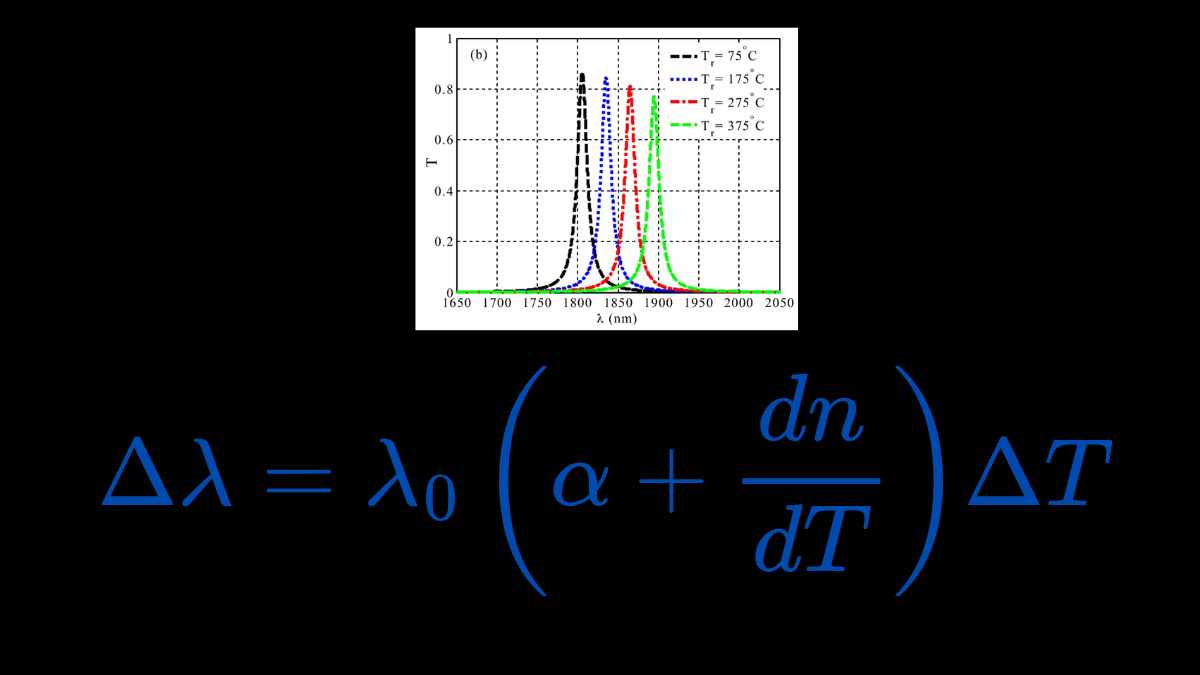
Temperature sensors based on one-dimensional (1D) topological photonic crystals (TPCs) represent an advanced class of optical sensors with high sensitivity and robustness against external perturbations. These sensors leverage the unique properties of topological edge states in photonic bandgap structures, offering advantages in precision, stability, and resilience to defects. Introduction to Topological Photonic CrystalsTopological photonic crystals […]
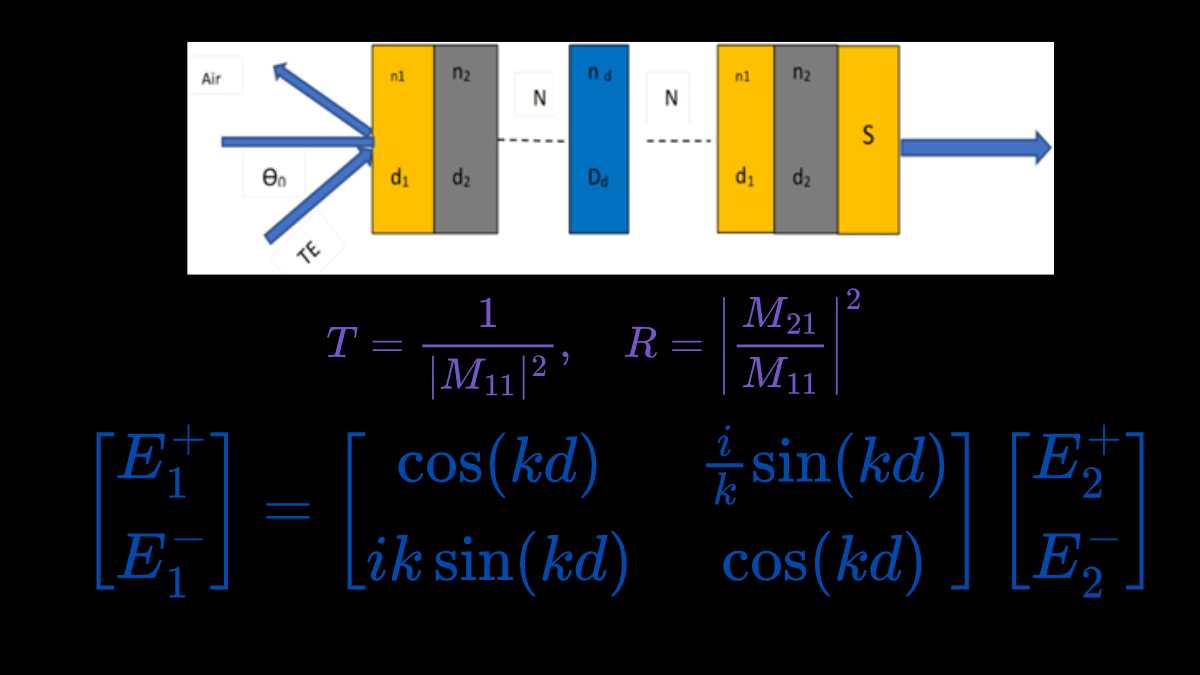
Photonic crystals (PhCs) are periodic dielectric structures that affect the motion of photons in much the same way that the periodic potential in a semiconductor crystal affects electrons. The ability of photonic crystals to create photonic band gaps (PBGs) has led to numerous applications, including optical filters, waveguides, and more recently, sensors. Among the various […]

The concept of large effective area in photonics plays a crucial role in various applications, particularly in optical fiber communications, high-power laser systems, nonlinear optics, and supercontinuum generation. The effective area ($A_{\text{eff}}$) of an optical waveguide defines the spatial confinement of the optical mode and is a key parameter influencing nonlinearity, optical damage threshold, and […]
